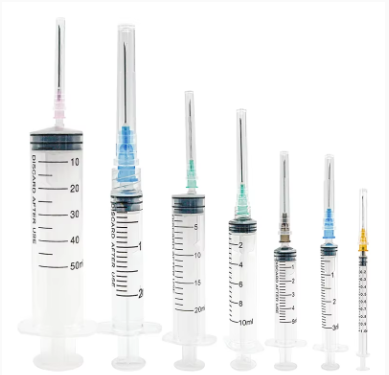
Understanding Syringe Sizes and Measurements
Choosing the correct syringe size is vital for accurate medication administration. Syringe sizes are measured either in milliliters (mL) or in specific units, such as insulin units, which are crucial for precise dosage calculations. To illustrate, one milliliter (mL) is equivalent to 100 insulin units, making understanding these conversions essential for healthcare practitioners to avert medication errors. Additionally, different medications may require distinct measurement systems. For example, some drugs are prescribed in milliliters while others need dosing in units, emphasizing the importance of comprehending syringe measurement units to ensure patient safety.
Key Measurement Units: mL vs. Units
For those working in healthcare, being familiar with syringe measurement units, like milliliters (mL) and insulin units, is necessary to prevent dosage inaccuracies. Conversions such as one mL equating to 100 insulin units are particularly relevant in diabetes care, ensuring insulin is administered correctly. This precise understanding prevents errors in dose calculations, which can have serious health implications. Furthermore, various medications could use different measurement systems, requiring doses in either milliliters or units, underscoring the need for healthcare practitioners to understand conversion methods thoroughly.
Standard Syringe Volume Ranges
Syringes are available in a range of standard volumes from as small as 0.3 mL to as large as 60 mL, each catering to specific clinical applications. Smaller syringes, such as those ranging from 0.3 mL to 3 mL, are typically used for injections that demand high precision. For procedures requiring larger volumes, such as irrigation tasks, syringes exceeding 5 mL are more suitable. Understanding these syringe volume ranges is imperative for medical professionals, who must select the appropriate size based on the medication being administered and the requirements of the practice setting.
Common Syringe Sizes and Their Uses
0.3mL Syringes: Precision for Small Doses
0.3mL syringes are especially useful for administering small doses of medication, such as insulin, where precision is crucial. These syringes are usually equipped with fine gauge needles, ranging between 30 to 31 gauge, which significantly minimizes discomfort and reduces tissue trauma for patients. This feature makes them ideal for patients who require meticulous dosage control without compromising comfort. Healthcare providers must select the correct syringe size to ensure safety and compliance with dosage requirements, thus preventing potential medication errors.
0.5mL Syringes: Versatility in Medication Delivery
The 0.5mL syringes strike a balance between dosage precision and usability, making them a versatile choice for medication delivery such as vaccine administration in pediatric patients. These syringes can be designed with different needle gauges to suit a variety of medications and patient needs. Selecting the appropriate syringe size is essential for enhancing both the comfort and effectiveness of medication administration. This versatility ensures that the 0.5mL syringes are adaptable across different medical settings and patient requirements.
1mL-3mL Syringes: Standard Applications
Syringes in the 1 to 3mL range are the most commonly used for various injections, including immunizations and routine medications. They offer greater volume control, which makes them suitable for both adult and pediatric patients requiring moderate dosages. Understanding the typical applications of 1mL to 3mL syringes helps healthcare providers make informed decisions on medication delivery, ensuring accurate dosage and improving patient outcomes. This standard range covers a broad spectrum of medical needs, highlighting its importance in everyday medical practice.
Larger Sizes (5mL+): Specialty and Irrigation Uses
Syringes greater than 5mL are often utilized for specialty procedures, including irrigation, feeding, or larger volume injections. These syringes may come with different tip styles, such as Luer lock or slip tip, to accommodate various medical devices and procedures. Understanding the applications for larger syringes ensures proper healthcare practices and patient care. By having a comprehensive grasp of the uses of these larger syringes, healthcare professionals can effectively manage situations that require more substantial volume and specialized syringe features.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Syringe Size
Medication Volume and Dosage Requirements
Choosing the right syringe size starts with understanding the medication volume and dosage necessary for effective treatment. The selection process is critical because inaccuracies in dosing can lead to adverse effects or therapeutic failure. For instance, using a larger syringe for small doses may cause precision issues, making accurate measurements difficult. Additionally, healthcare providers must consider the medication's viscosity, impacting how easily it can be drawn into the syringe. Denser solutions may require syringes designed to accommodate thicker fluids. Therefore, a well-informed choice is indispensable for ensuring proper dosage delivery.
Injection Type (Subcutaneous, Intramuscular, etc.)
Understanding the type of injection required is fundamental in syringe and needle gauge selection. Different injections, such as subcutaneous or intramuscular, necessitate different syringe sizes and needle thicknesses. For example, intramuscular injections typically warrant larger syringe sizes due to the higher volumes involved than those used in subcutaneous injections. Properly identifying the injection technique and anatomical site ensures that the chosen syringe will deliver medication effectively and comfortably. This tailored approach is essential for achieving optimal patient outcomes, as the wrong syringe size can diminish therapeutic effectiveness.
Patient Age and Physical Characteristics
The patient's age and physical characteristics, such as body mass index (BMI), heavily influence syringe size selection. Pediatric patients, for example, require smaller syringes to ensure comfort and dosing accuracy, while adults with larger body frames may need larger syringes for effective medication administration. Tailoring the syringe choice to individual patient requirements enhances safety and ensures that the healthcare experience is both comfortable and effective. This personalization in healthcare practices is vital for maintaining patient trust and compliance throughout the treatment process.
Specialized Syringe Types and Their Applications
Insulin Syringes: Matching Needle Gauge to Dose
Choosing the appropriate insulin syringe is crucial for diabetes management. Insulin syringes are uniquely designed to deliver insulin with precision, utilizing different gauge needles aligned with dosage needs. Generally, a smaller gauge needle, which corresponds to a higher number, is preferred for less painful injections—an essential feature for patients who require frequent insulin administration. Healthcare professionals play a vital role in educating patients on selecting the right insulin syringes to promote effective blood glucose management and patient compliance.

Safety Syringes: Needle Protection Features
Safety syringes have become essential tools in healthcare settings, equipped with needle protection features to minimize needlestick injuries—a significant concern for healthcare workers. These syringes commonly feature retractable needles or shields that engage immediately after injection, greatly reducing the risk of accidental injuries. Healthcare facilities must be aware of the available safety syringe options, not only to safeguard their employees but also to enhance patient safety. By utilizing syringes with robust needle protection mechanisms, healthcare providers can significantly lower the incidence of needlestick injuries, contributing to a safer healthcare environment and improving overall health outcomes.
Prefilled and Dual-Chamber Syringes
Prefilled syringes offer notable convenience by being preloaded with medication, which reduces preparation time and decreases exposure risks associated with handling. In contrast, dual-chamber syringes facilitate the co-administration of two incompatible substances, enhancing the efficiency of medication delivery. Healthcare providers should understand the applications of these specialized syringes to optimize medication management practices. For patients and medical personnel alike, these syringes represent an advancement in achieving convenient, efficient, and safe medication administration. Harnessing the benefits of prefilled and dual-chamber syringes can streamline treatment processes, offering a significant improvement in overall healthcare delivery.
FAQs About Syringe Sizes
How Do I Convert Between Units and Milliliters?
Converting between units and milliliters is crucial for precise medication dosing. This knowledge is especially important for medications like insulin, where dosage is often prescribed in different units. Healthcare providers must be adept at conversion factors—for instance, in insulin administration, 1 mL is typically equivalent to 100 units. Miscalculations in these conversions can lead to significant medication errors, compromising patient safety. Therefore, healthcare professionals must thoroughly understand these conversions to ensure safe and effective care.
Can I Use the Same Syringe Size for Different Medications?
Using the same syringe size for multiple medications can seem convenient but poses significant safety risks, particularly for high-risk drugs. Different medications may interact with residuals from prior uses, which could alter their efficacy or safety. For example, specific medication residues left in a syringe can cause adverse reactions if a different medication supersedes it. To prevent medication errors and ensure safety, healthcare professionals must educate patients on the importance of using dedicated syringe types or sizes for each medication, thereby enhancing overall medication safety.
What Size is Best for Pediatric or Geriatric Patients?
The ideal syringe size for pediatric or geriatric patients hinges on diverse factors, including body size, medication dosage, and the method of injection. Children, given their smaller stature, often require smaller syringes to ensure precise dosing and comfortable administration. For the elderly, selecting syringes that prevent unnecessary pain is critical due to their often thinner skin and increased sensitivity. This attention to detail in syringe selection not only ensures accurate medication delivery but also significantly enhances the experience for these sensitive patient groups by prioritizing their comfort and safety.